What Is Metabolism?
Metabolism is the entire suite of biochemical processes that occur within living organisms whose goal is to change food into energy by either breaking something down (catabolism) or building something up (anabolism). Cells convert relatively simple nutrients into energy and building blocks needed for growth and survival.
The term “metabolism” refers to all the reactions that occur in an organism. This includes the actions of our digestive system, circulatory system, nervous system, immune system, endocrine system, etc. Thousands of metabolic reactions happen at the same time to keep our cells healthy and working, all of which are regulated by the body.
Metabolic rate is the frequency of the metabolic pathways or the amount of energy that is used by an organism to maintain itself.
There are compounds/entities that can either support healthy metabolism (pro-metabolic) or things that harm it (anti-metabolic).
But first, we need to discuss a little bit about metabolism, and why there are so many misconceptions about it today.
Warburg Metabolism & Cancer
At the Max Planck Institute in the 1920s, Dr. Otto Warburg was the first person to discover that cellular respiration took place in tiny structures he called “grana,” which later became known as mitochondria. While there, Warburg tested the effects of alcohols, cyanide, and other chemicals on respiration. Through his testing, he concluded that the enzymes in the “grana” must contain a heavy metal. He suspected, and later proved that that heavy metal was iron- in the form what we now know as hemoglobin.
Warburg went on to conduct experiments using spectrophotometry, which is a method to measure how much a chemical substance absorbs light by measuring the intensity of light as a beam of light passes through sample solution.
Warburg went on to find that the enzyme that reacts with oxygen in a cell is identical with the portion of hemoglobin that binds oxygen in the blood. That compound is called heme.
Heme is porphyrin. Porphyrins are a group of organic compounds that play a crucial role in various biological processes. They are characterized by a large, cyclic structure composed of four modified pyrrole rings linked together. The core structure is known as porphine (pictured below).
Aside from this discovery, Warburg is more famously known for his work in the field of cancer. He thought that because cancer cells divide so rapidly that they must utilize more oxygen. To his surprise, he ended up discovering the exact opposite. Tumor cells appear to use considerably less oxygen compared to healthy ones. Warburg found that if healthy cells were deprived of 35% of their normal oxygen intake, every single one of them would turn cancerous.
To understand this, we need to understand what respiration looks like without oxygen. This is known as anaerobic glycolysis (sometimes shortened to just “glycolysis,” which can be confusing), or fermentation. Fermentation is the process of breaking down sugars (glucose) into acids (like lactic acid) or alcohol (ethanol) without oxygen. In humans, fermentation is considered to be highly inefficient and only becomes important when little to no oxygen is available.
Fermentation is thought to be an older form of metabolism because it is present in all lifeforms, even before plants appeared on Earth and filled the atmosphere with oxygen. Many bacteria and yeasts still rely on fermentation to produce energy today.
What Warburg found is that cancer cells are different from normal cells in all organisms because they fundamentally maintain higher rates of anaerobic glycolysis (fermentation) and produce large amounts of lactic acid, even when oxygen is present. This discovery eventually became known as the “Warburg Effect.” This concept is used to this day for diagnosing and staging cancer using PET (positron emission tomography) scans.
Because fermentation is inefficient and consumes glucose at a tremendous rate, PET scans can easily find tumors in the body when patients are given radioactive glucose. The more malignant the tumor, the more rapidly it takes up glucose.
In 1931, Otto Warburg received the Nobel Prize for showing that cancer cells get energy by fermentation the same way fungi (and many bacteria) do.
Warburg was able to repeat his experiments enough that he felt confident the cause of cancer was damage to the respiratory mechanisms in the cell, leading to unchecked glycolysis.
Unchecked glycolysis = unchecked growth = tumor growth (cancer)
Warburg felt all complex organisms must have enough oxygen to maintain health, “The causative factor in the origin of tumors is nothing other than oxygen deficiency.”
His theory was kind of pushed to the wayside when others were finding that certain chemicals were linked to cancer. Many scientists at the time were hesitant to believe in a common cause that was so simple. Warburg’s retort was that each of these thousands of chemicals all eventually starve the cells of oxygen in their own way.
By 1942, Dean Burk at the National Cancer Institute was able to report that this was true of over 95% of the tumors he examined. Because he felt he knew what the cause of cancer was, Warburg thought that you could prevent 80% of all cancers if you could keep out the known carcinogens.
In 1966, Warburg stated, during a lecture…
“Cancer, above all other diseases, has countless secondary causes. But, even for cancer, there is only one prime cause. Summarized in a few words, the prime cause of cancer is the replacement of the respiration of oxygen in normal body cells by a fermentation of sugar. All normal body cells meet their energy needs by respiration of oxygen, whereas cancer cells meet their energy needs in great part by fermentation. All normal body cells are thus obligate aerobes, whereas all cancer cells are partial anaerobes. From the standpoint of the physics and chemistry of life this difference between normal and cancer cells is so great that one can scarcely picture a greater difference. Oxygen gas, the donor of energy in plants and animals is dethroned in the cancer cells and replaced by an energy yielding reaction of the lowest living forms, namely, a fermentation of glucose”
Translated into modern language, what Warburg called a shift towards anaerobic glycolysis (fermentation) is known today as mitochondrial dysfunction.
I think he’s right. It is unfortunate that Warburg passed away in 1970. 1970 happened to be the year the first oncogene was discovered, which started the radical shift towards the belief that cancer was caused by genetic mutations and not by altered metabolism.
The problem is this theory seems to have no legs even 50 years after its discovery.
Even the National Cancer Institute says that no more than 10% of all cancers can be “genetic.” Actual research shows that 5% of cancers (if that) are actually “genetic in nature,” and the confirmation by PET scan actually proves Warburg to be correct.
Yet we keep looking for genetic answers to a mitochondrial problem…
Shifting Gears
If you don’t know, Dr. Warburg is the guy who credited Max Planck with the ever-famous line that science progresses not because scientists change their minds, but rather because scientists attached to erroneous views die and are eventually replaced. In Western $cience, not much has really changed.
There is no cancer that exists today that has healthy cellular respiration. This is one thing ALL cancers have in common. Yet modern $cience continues to spend billions of dollars searching for some sort of genetic reason behind cancers.
What became clear from Warburg’s work is that a relative lack of oxygen, from any cause, creates an environment for cancer cells to thrive. Cancer takes a while to develop, and things are usually going wrong for a while before it can even be picked up by modern-day technologies. This is because there is some degree of mitochondrial dysfunction because of a relative lack of oxygen, or pseudohypoxia.
Warburg found that if high oxygen pressures are available, cancer progression completely stops and aerobic metabolism (the ETC) returns in chicken embryos.
When in a pseudohypoxic state, the use of fermentation and the pentose phosphate pathway become more prominent for energy. The pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) generates NADPH, the major source of reducing equivalents in the protection of RBCs against oxidative injury. The PPP is also used to generate DNA and RNA. These two pathways are designed to function in a low oxygen environment.
These are great when needed but are not meant to be relied on indefinitely. If so, you can run into issues with apoptosis and autophagy. Apoptosis and autophagy are important molecular processes that we need to maintain our health. Apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process of cell death that occurs naturally in multicellular organisms. It helps eliminate cells that are no longer needed or have become a threat to the organism. Autophagy, meaning “self-eating,” is a cellular recycling process that involves the degradation and recycling of cellular components, including organelles and macromolecules. Autophagy is crucial for recycling damaged cell parts and cellular debris.
Inactivation of apoptosis and autophagy leads to cancer over time. Stressors like blue light and nnEMFs inhibit the function of autophagy and apoptosis- thus your ability to use oxygen.
Functionally, when you lose control of autophagy and apoptosis, cancer is the result. Sunlight helps mitochondria and cells regain their autophagy and apoptosis abilities.
nnEMFs are widely recognized for their ability to interfere with the regulation of calcium and calcium-gated channels. They can influence what can enter or exit mitochondria. This implies that tumor-causing changes can occur without ionizing radiation. When this happens, mitochondria can release more extremely low-frequency ultraviolet (ELF-UV) light from the cell compared to normal conditions.
Man-made blue light devices are different from naturally occurring light because they create relative oxygen deficiency and modifying free radical signaling within cells. This is universally accepted when it comes to x-rays, but not taken seriously when it comes to blue light. In other words, different forms on nnEMFs, not just ionizing x-rays and gamma rays, can play a role in mitochondrial dysfunction, altered metabolism, and eventually cancer.
What Fritz Popp found was that when cells were shifted more towards fermentation, they would release excess ELF-UV light. He found that mice transplanted with cancer had a greater biophoton emission than healthy models. In fact, they found a correlation with biophoton intensity and growth rate observed, representing the higher metabolic activity of cancer cells and the state of oxidative stress in cancer cells.
In other words, the better the mitochondrial redox, the less of a chance for “mutations” to occur. What blue light does is lower the oxygen tension in cells. When oxygen tension is low, it changes free radical signaling in cells and can ultimately lead to cancer.
As we have learned from a previous blog…
Decreased mitochondrial function = an increase in heteroplasmy rate = Faster aging & dis-ease
Mitochondrial Function
As you may recall, heteroplasmy describes the situation in which two or more mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) variants exist within the same cell.
You can have up to 70% heteroplasmy rate and still maintain “healthy” cell function. Increased heteroplasmy rates are associated with a vast array of health challenges, including many of the chronic dis-ease we see today.
- Cancer
- Heart disease
- Diabetes
- Kidney disease
- Autoimmune challenges
Heteroplasmy rates increase when the redox potential of the mitochondria are diminished. Blue light and nnEMFs are two potential causes of increased heteroplasmy rates.
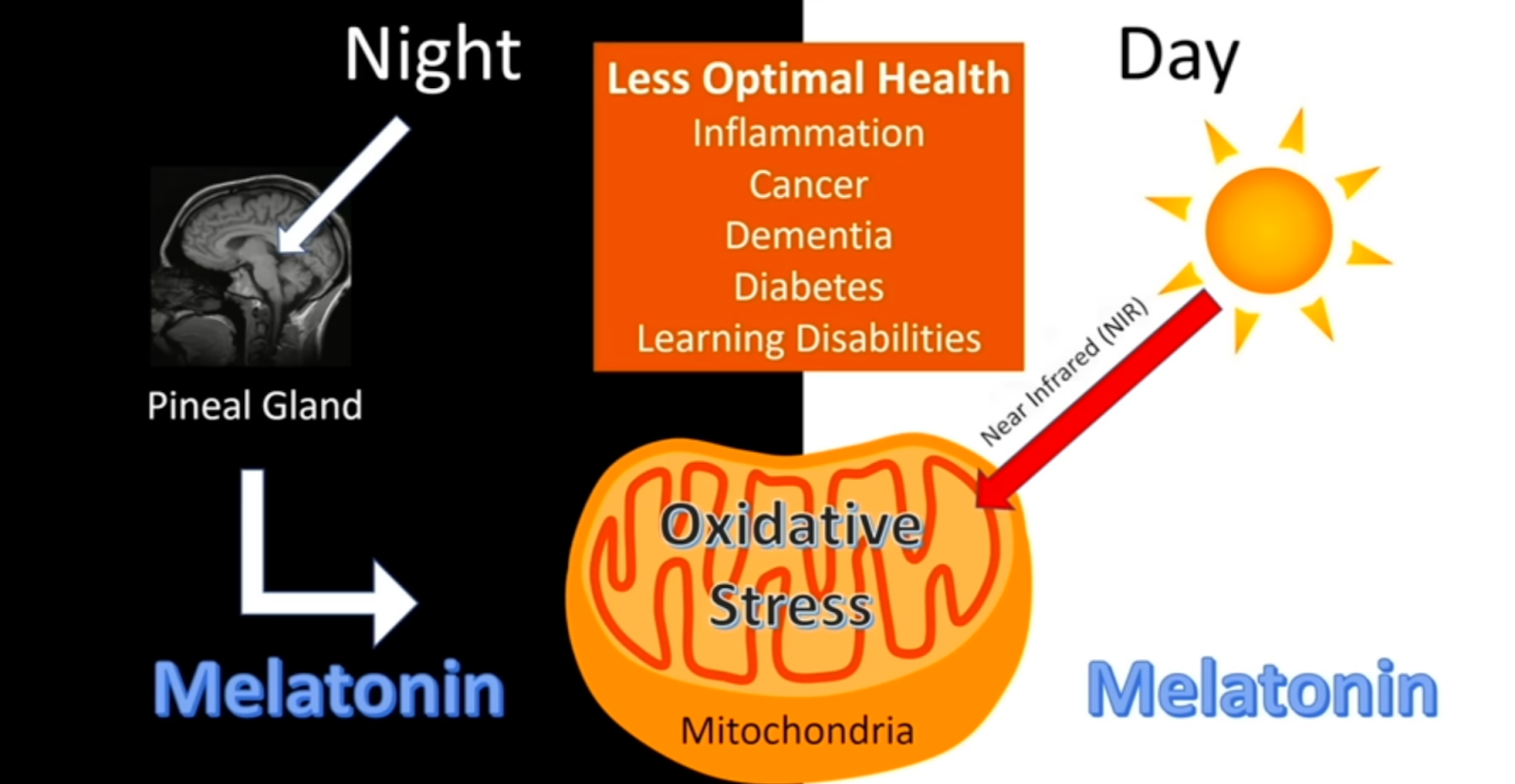
Part of this has to do with melatonin production and the fact that 95% of it is located in the mitochondria. As we have learned, improper light environments can impact the body’s ability to create sufficient melatonin. When there isn’t enough melatonin in cells, it can lead to greater ELF-UV light but also increased heteroplasmy rates and cancer.
Our mitochondria are finely tuned to interact with our Natural environments and sunlight. When we are constantly surrounded by nnEMFs, we can lose our ability to efficiently burn fat, irrespective of dietary choices. This is because our five senses did not evolve to detect these artificial sources.
All light waves undergo transformation into electro-mechanical waveforms within a cell. The amount of natural EMFs and nnEMF in the environment changes the sizes and shape of its own respiratory proteins and the distances between them. This informs them to remain inactive or become responsive.
All of this to say a robust mitochondrial redox potential comes from how good a signal we have to sunlight and our Natural environment.
The water in our cells and mitochondria is not the same water you find in your glass. Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are mirrors. Mitochondria create water because they reverse the process of photosynthesis, which consumes water. When that water is not structured, you will not get the exclusion zone you need to propel reactions in the body. The hydrogen bonds are weaker, and the networks become more spread out, making it difficult to transmit signals. When the cellular respiration proteins of the mitochondria are more spread out, electron tunneling becomes less effective, and their redox power diminishes.
A Light Story
Light travels in a twisting spiral pattern. This is due to its electric field consistently being orthogonal (90 degrees) to the magnetic field in an electromagnetic wave. This also means that light traveling interacts with any object or medium it spirals.
In humans, light tends to spiral clockwise, which may explain why chirality exists in Nature.
Eukaryotic cells function optimally within the 0-200Hz range and the visible spectrum of sunlight.
Red light wavelengths improve electron flow in the ETC, and allow the enzymes to function at 100% efficiency.
Infrared wavelengths allow for more charge separation, creating a more “powerful” battery. Bigger battery = more energy.
The Modern world operates on a much different level than the Earth’s magnetic field.
Certain proteins in the body are able to resonate with certain wavelengths of light. For example, the initial cytochrome in mitochondria is a fluorophore protein absorbing light at 340nm (NAD+/NADH couple). As you can see in the picture below, UV light does not penetrate very deeply below the skin’s surface.
You may ask yourself, “Why would mitochondria use a light frequency that wouldn’t penetrate that deep in the body?” It is from food electrons, the bio-photon field during the night.
When we consume food, it transforms into excited electrons and protons, with electrons becoming excited through sunlight during photosynthesis. Electrons continuously reach the inner mitochondrial membrane to enter the Electron Transport Chain (ETC) when we eat.
However, in direct sunlight, ATP can be generated without the need for food electrons. In the absence of food intake, exposure to UVA and IRA light stimulate specific mechanisms. UVA light in the eye and skin generates nitric oxide (NO), inhibiting cytochrome C oxidase function, while red light aids in moving H+ through the ATPase as oxygen levels decrease. Both can alter the speed of the ETC. In sunlight, because there is a full spectrum of light, you find the balance that is ideal for the given time of day.
When the body senses incident light that isn’t sunlight, it leads to a decline in energy production within the mitochondria, known as the Warburg shift. The Warburg shift is a transition from oxidative phosphorylation to rapid aerobic glycolysis (known as the Warburg Effect) that goes along with a high rate of lactate production.
The Warburg Shift results in a loss of fat burning, and mitochondria must revert to older pathways of glycolysis and glutamine catabolism for energy production. As more mitochondria are damaged, the more you will see this effect occur.
This happens when there are low levels of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) and low oxygen tension. This mimics the behavior of obligate glycolytic cells such as red blood cells (RBCs- they don’t have any mitochondria to use oxidative phosphorylation). Interestingly, you don’t see a large change in oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) signaling until oxygen tensions rise.
Understanding how sunlight affects the inner mitochondrial membrane is crucial for comprehending why a deficiency in solar light necessitates more food to fuel electron transport chain flow to oxygen. Light is carried indirectly by electrons and protons through food via sunlight.
When you are stressed, mitochondria accumulate calcium in an attempt to recalibrate the inner mitochondrial membrane. If this doesn’t work out, mitochondrial stress intensifies, leading to increased size and higher heteroplasmy rates. Calcium influx also elevates oxygen consumption, creating a relative pseudohypoxia at the tissue level, activating calcium-activated dehydrogenases and mitochondrial nitric oxide synthase (mtNOS), which decreases oxygen consumption as nitric oxide competes with cytochrome C oxidase.
So at the end of the day, it comes down to optimizing your mitochondria’s ability to utilize oxygen.
So How Do You Optimize It?
Luckily, there’s a lot you can do to bring your metabolism back online.
Filter Out Excess Lactic Acid
As mentioned above, lactic acid buildup and a shift toward fermentation is not going to be good for your metabolism. Lactic acid opposes the protective effects of CO2 (which is our primary stimulus to breathe). Too much lactic acid is associated with seizures, heart failure (associated with premature aging of the heart, a concern for athletes), calcification of tissues, and negatively impacts the liver and kidneys.
The first thing you would want to do is boost your CO2 levels by starting to nasally breathe. We’ll touch on this in future blogs. For now I have an entire course on how to do this.
You also might want to consider avoiding fermented foods, including beer, for a while, as they contain lactic acid. Bacterial lactic acid, found in fermented foods like kimchi, yogurt, and sourdough, can be more problematic than the type produced under conditions like exercise, making their consumption unfavorable.
Ditch the Poor-Quality Oils
Processed seed and vegetable oils are ubiquitous nowadays. 95% of all packaged processed foods will have some form of processed garbage “foods,” if you can even call them that.
But first, a little clarification. Not all seed oils are bad, but the ones that are should not even be considered foods. Unlike traditional oils extracted from olives (technically a fruit oil) or coconut, squeezing seeds yields nothing.
These seed oils most influencers refer to are GMO soy, cotton, and rapeseed (canola), most of which owned primarily by just a few companies if you follow the money.
To create oils from the seeds, they undergo high-temperature heating, causing oxidation and the formation of potent and carcinogenic byproducts.
This is particularly concerning for cancer patients and should not be ignored since they are going to really struggle with recovery if they keep eating these oils. They can end up in cell membranes and really mess with metabolism, which is important since cancer results from dysfunctional metabolism.
Once the seeds are heated, they are then proceeded with petroleum-based (yes, petroleum) solvents, usually hexane, to maximize the oil extraction. Other chemicals are then used to deodorize oils that smell, and others may be added to enhance color.
They all deplete antioxidants (vitamins A, C, E, zinc, selenium, magnesium, etc.), increase estrogen, unbind iron and have a myriad of negative effects on our health.
Believe it or not, poor quality fats are a more significant contributor to diabetes than sugar (we covered other causes in this blog post), primarily due to their role in the oxidative destruction of mitochondria, crucial for processing carbohydrates for energy. This is done by blocking the pyruvate dehydrogenase enzyme.
Poor-quality fats and seed oils have unique ways they mess with your digestion. In fact, they directly destroy the ability to digest and absorb food.
It’s not just the poor-quality fats, either. Any food (or food like products) that can negatively impact your ability to absorb nutrients can directly or indirectly lead to health problems of all kinds.
If your digestion is impaired, then dysfunction isn’t far behind.
- Stop consuming these poor-quality fats and oils
- Whole fats are generally better fat sources than oils (whole olives or coconuts vs. their respective oils)
- If you are going to use oils, limit them to extra virgin olive oil, coconut, and/or avocado
- Increase intake of fat soluble vitamins (vitamin A, D, E, K) and vitamin C
- Sauna sessions 2-3 times a week for 10-20 minutes are helpful
- Sweaty exercise sessions 2-3x/week is great
- Gradually reduce body fat if above 14% for males and 17% for females
- Incorporate bee pollen, acerola cherry, pomegranate, or other whole food antioxidant sources (ideally a variety of them)
- Optimize thyroid performance for overall health and well-being
Identify and Address any Heavy Metal Sources
Mitochondria are primarily where metabolism “rubber meets the road.” Wouldn’t you know it, heavy metals wreak havoc here too. They do this by altering mitochondrial membrane permeability and generating increased amounts of reactive oxygen species (ROS). When left unchecked, this can cause damage to the respiratory chain, inhibit ATP production, cause oxidative phosphorylation decoupling, and potentially mitochondrial apoptosis.
Chronic mercury exposure can lead to mercury building up in mitochondria. Heavy metal accumulation can impact ATP production and the calcium balance in the mitochondria, leading to problems.
Heavy metals like mercury and arsenic can also alter mitophagy (the mitochondria’s version of autophagy).
Lead is a neurotoxin, and it is well established that it disrupts normal nervous system function. It is associated with reduced IQ, anxiety disorders, and depression. Lead also messes up the balance of the redox system, inducing an inflammatory response in many organs by way of lipid peroxidation. Lipid peroxidation is a process under which oxidants such as free radicals damage lipids containing carbon-carbon double bond(s),
Cadmium causes severe damage to the lungs and kidneys, and is known as a carcinogen. The most common sources of cadmium are conventional grains and tobacco.
Aluminum technically isn’t a heavy metal by definition (something at least 5x the specific gravity of water), but nonetheless causes a lot of problems and sometimes gets lumped into this category. Aluminum is a neurotoxin known to cross the blood-brain barrier. As you might expect it is linked to mostly neurological diseases (remember, oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction cause neurodegeneration). As far as ditching aluminum, the first thing I would do is replace any aluminum cookware you own. I would also throw out/replace any conventional cosmetic/self-care products such as deodorants, shampoos, and toothpastes. Luckily, there are many alternatives for these today. You might also find aluminum in some cheeses and baking soda that does not claim to be aluminum-free.
Arsenic is linked to many different types of cancer, include lung, bladder, and skin cancers. The most common exposures to arsenic come from unfiltered water, certain seafoods, and rice products that are not organic. There will still be trace amounts of arsenic in organic rice, so it’s important to soak rice overnight, drain it, and rinse it before you cook it.
Mercury is another heavy metal that causes quite a few neurological problems because it is able to cross the blood-brain barrier. The most common exposure to methylmercury occurs when folks consume fish like tuna and swordfish. If your dentist is telling you that mercury amalgams are safe, then it’s time to find a new dentist.
Perhaps the most common offender we deal with as Modern Humans is unbound iron. We of course need iron to help mobilize oxygen and carbon dioxide in the body, but too much iron also isn’t good. Unbound iron causes a great deal of oxidative stress and can impair metabolism. Iron itself isn’t exactly a problem. It can become problematic when it is in its free (unbound) form because it can redox reactions, iron is a catalyst for the formation of hydroxyl radicals from reduced forms of oxygen.
Those who are anemic don’t necessarily have to consume more iron. In most cases (I’d say over 90%), anemia isn’t caused by a lack of iron intake outright. Rather it is poor absorption or digestion of food OR a deficiency of other nutrients that are involved in iron metabolism, like vitamin A, vitamin D (sunlight), biotin, and vitamin C.
I have an entire course on how to detox heavy metals safely and effectively, and you can check it out here.
Excess Estrogens
Most endocrine disruptors work by creating an imbalance in your sex hormones by increasing the amount of estrogens. This occurs for both men and women, the main difference being the common symptoms. Estrogen, especially synthetic forms, can inhibit pyruvate dehydrogenase and block the function of cytochrome C oxidase.
The list of problems caused by excess estrogens can be far reaching.
- Inhibit the thyroid hormone secretion
- Elevates nitric oxide
- Encourage the retention of iron
- Damages the adrenals (cortex)
- Trigger the release of histamine
- Excess can act as an antagonist for vitamin E and magnesium.
- Contribute to the development of osteoarthritis.
- Can lead to infertility
- Increase the risk of miscarriages
- Lowers testosterone and progesterone.
- Contributes to the onset of depression, anxiety, and panic disorders
- Lower the seizure threshold of nerve cells.
- May potentially lead to dementia
- Excess is carcinogenic
- Accelerate the aging process of skin and tendons (note: progesterone has been observed to reverse certain cases of tendinitis in menopausal women).
- Contribute to chronic fatigue (certain forms of estrogen negatively impact NAD/NADH).
- Depletes zinc
Men and women need estrogens in the right amount. The problem is that excess estrogen exposures are so common today. The main offenders are xenoestrogens, poor quality fats, cosmetics, self-care products, plastics, and other items containing parabens and phthalates. Make sure you’re detoxifying as well as possible, use herbals or binders if necessary, and get outside in the sun. This is the starting point.
Too Much Nitric Oxide
I talk about nitric oxide (NO) a ton in my Breathe Easy Masterclass, but did you know it is an ROS? ROS get a bad rap but they do have some really important functions in the body (see this blog), including cell signaling, boosting mitochondria function, immune system function, and cellular adaptation.
Nitric oxide is produced by a group of enzymes called nitric oxide synthases. Nitric oxide has various roles as a signaling molecule in vasodilation, neurotransmission, and immune response. It can have beneficial or harmful effects depending on its concentration levels.
Too much NO can accelerate aging because it impairs mitochondrial function (slows down Cytochrome C Oxidase). There are many things that can lead to excessive nitric oxide production, including…
- ED drugs or supplements
- Pre-workout supplements
- Lack of antioxidant
- Lack of sulfur containing foods
- Gut problems
- Tap water
- Lack of sunlight
- Mouth breathing
- Artificial light at night
- Estrogen dominance (in men AND women)
So to optimize NO production, it really starts with doing the opposite of what is listed above.
- Daily sunlight on bare skin and eyes
- Address any gut issues
- Nasal breathing, all day and night (if you have sleep apnea or trouble with this, check out the course)
- Reduce artificial light at night
- Remove/eliminate excess estrogens
- Get a water filter (particularly one that can filter out fluoride)
- Eliminate the usage NO products and pre-workout
Excess Stress Hormones
To put it simply, stress can damage both nuclear and mitochondrial genes. Raising cortisol is vital and life-saving short-term, but can cause some real problems long-term.
Short-Term
Cortisol is a life sustaining adrenal hormone:
- Blood sugar levels
- Enhances fat, protein and carbohydrate metabolism
- Enhances immune responses
- Anti-inflammatory actions
- Raises blood pressure
- Alters heart and blood vessel tone (more blood to the muscles and nervous system, less to digestive and eliminatory organs)
- Activates the central nervous system
Long-Term
Higher and more prolonged levels of circulating cortisol…
- Initiates pregnenolone steal
- Diminishes cellular utilization of glucose
- Increases blood sugar levels
- Decreases protein synthesis
- Increases protein breakdown that can lead to muscle wasting
- Causes demineralization of bone that can lead to osteoporosis
- Interferes with skin regeneration and healing
- Causes shrinking of lymphatic tissue
- Diminishes lymphocyte numbers and functions
- Impaired cognitive performance
- Dampened thyroid function
- Blood sugar imbalances
- Decreased bone density
- Sleep disruption
- Decreased muscle mass
- Elevated blood pressure
- Lowered immune function
- Slow wound healing
- Increased abdominal fat
- Depression, lupus, migraine, menopause, diabetes, aging, and MS
Long story short, over time, stress will lead to deficiency in all of your protective steroid hormones.
So remember to take care of yourself. Avoid/limit alcohol, get plenty of sleep, ground daily, get sun daily, minimize nnEMF exposure, make sure you exercise regularly but don’t overdo it (it’s better to break your workouts into more sessions with less volume, than it is to burn yourself out), and don’t consider fasting if you are not metabolically ready for it.
Balance Thyroid Hormones
Thyroid hormones go hand-in-hand with adrenal function. In fact, I think most of what we call hypothyroid is actually HPA-axis dysfunction, adrenal fatigue, or whatever other name you have for it.
Every cell in the body depends upon thyroid hormones for regulation of their metabolism. Thyroid is the gas pedal of the body.
What we do know is that the thyroid governs the speed of your metabolism. Healthy thyroid function is needed to optimize sex hormones testosterone, estrogen, DHT, and others.
The principal hormones it makes are thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which is more active. These hormones regulate the growth of many systems in the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine.
Fluoride can be a major issue here as well. Fluoride is harmful because it blocks water semiconduction in the body, which ruins cell signaling and can cause cancer. Fluoride is the most electronegative element in the periodic table, meaning it easily attracts a pair of electrons to form a chemical bond.
Since oxygen is the next most electronegative atom, that means it can compete with oxygen to cause a litany of issues all over the body. Nazi scientists knew this and experimented with different formulas containing fluoride in concentration camps. They found it made the prisoners more “docile.”
Fluoride is known to impact the cardiovascular, central nervous, digestive, endocrine, immune, integumentary, renal, and respiratory systems, and exposure to fluoride has been linked to Alzheimer’s disease, cancer, diabetes, heart disease, infertility, and many other adverse health outcome.
I’d highly recommend getting a filter that can filter fluoride out of your water as best as possible. We currently use a Clearly Filtered System and an AquaTru system (code to save here). I also like Berkey, and I’m sure there are other solid ones. No matter what, make sure that you find one that can filter out fluoride.
Sunlight
There’s an entire blog series on this topic already. It baffles me how this is the first week of 2024 and most people still think the sun is harmful to them.
I often think that simply observing Nature and mirroring it goes a long way. The flourishing of Spring. The release of Fall. The stillness and hibernation of the Winter. It’s all there. But simply observing this should give you a glimpse of the role sunlight plays in Nature.
It is downright hilarious how people can think the source of all life on this planet is somehow harming them. Just so you have an idea, the sun…
- Regulates your circadian rhythm
- Regulates every metabolic process
- Optimize vitamin D stores
- Improves insulin resistance independent of food
- Improves sex hormone balance
- Helps with acne, psoriasis, burns, eczema, and other skin disorders
- Regulates muscular stimulation and relaxation
- Improves Seasonal Affective Disorder
- Lowers high blood pressure
- Decreases high cholesterol
- Lowers high blood sugar in diabetics
- Increases white blood cell counts
- Improves cardiac output
- Improves blood oxygen carrying capacity
- Reduces body odor
- Boosts the body’s immune system
- Boosts metabolism
- Reduces Bacteria count by as much as 50% from infections
- Decontaminates blood transfusions
- Improves DNA repair
- Irradiates the blood of cancer patients
- Improves symptoms of hyperbilirubinemia (neonatal jaundice)
- Improves kidney function
Since our skin is made out of the things we put in and on our bodies, if you consume garbage toxic, pro-inflammatory foods (poor fats, processed sugars, dairy, etc.), alcohol, tobacco, marijuana, and other stressors, you will be more prone to skin damage.
In modern environments today, if you do not get enough sunlight, the exposure to blue light alone is enough to cause issues with glucose metabolism and contributes to insulin resistance.
Most conventional medicine ignores that lack of sunlight suppresses thyroid hormone and progesterone (which balances estrogen and testosterone) production. They ignore that most people are already deficient in vitamin D and are more willing to throw supplements at a problem for fear of using the sun to heal.
If you haven’t been out in the sun in a while, then gradually build up your skin callous over time. It is important to understand that the sun alone does not (and never has) cause cancer. You need daily exposure, and you need to support your body with regular exposure and healthier lifestyle choices…
B Vitamins
This is a gross simplification, but generally speaking your B1, B2, B3, and B5 vitamins are your “energy” B vitamins. B6, B9 (folate) and B12 are more used in methylation. There is some overlap, so take that with a grain of salt.
In short, B vitamins are really important for healthy metabolism. In fact, you can find the names of some of these in the vitamins you need!
1) Thiamine (B1) is essential for TPP (Thiamine pyrophosphate)
2) Riboflavin (B2) is essential for FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide)
3) Niacin (B3) is essential for NAD (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide)
4) Pantothenic acid (B5) is essential for CoA.
All of these (and others) are needed for a healthy Citric Acid Cycle. The TCA cycle is what you need for healthy mitochondrial function to create energy, water, and ATP.
If you’re looking for (in my opinion) the best sources of these foods, then refer to the list below.
B1: Found in many food sources, such as beans, seeds, oats, brown rice, certain yeasts, lentils, potatoes, oranges, green leafy vegetables, nuts, and peas. Chlorinated water and black teas may destroy thiamine.
B2: Green leafy vegetables, beans, mushrooms, almonds, green vegetables, rice bran, avocados, grains, sunflower seeds, Brussels sprouts, prunes, beet tops, turnips, apples, bananas, carrots, grapefruit, kelp, coconut.
B3: Wheat germ, nuts, brown rice, sunflower seeds, potatoes, green vegetables, almonds, rhubarb, whole barley, rice bran.
B5: Peas, royal jelly, green vegetables, avocados, bananas, dried mushrooms, broccoli, collard greens, oranges, legumes, and sunflower seeds.
Carbohydrates Are Your Friend
I understand most people talk using the macronutrient lingo, but until more people realize that nutrition has more to do with the movement of protons and electrons and not fats, carbs, and proteins, we’ll have to keep translating.
Carbohydrates are simply organic compounds that consist of carbon, oxygen, hydrogen and are pro metabolic. The term “carbohydrates” refers to a group of chemical substances made up of carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen (carbon and water). They include starches, sugars, glycogen, dextrins, and celluloses.
Carbohydrates are grouped by the number of carbon atoms they contain and by the combinations of sugars. Since organic carbon compounds supply the main energy source for cells, these carbohydrates are used by your body for its primary energy supply.
All green plants use the sun’s energy to combine carbon dioxide and water to form carbohydrates. This is known as photosynthesis. Cellulose, the chief component of plant cell walls of plants, is an example of carbohydrate. When humans consume plants, the cellulose acts as a broom and energizer to the cells of the intestinal walls. This is why the consumption of fiber is so important for your health and the vitality of the digestive tract!
If you stick to carbohydrates that come from Nature directly, you’re going to be in good shape with time. If you feel as if you are “carb intolerant” then there is likely an underlying pancreas or digestive tract weakness and fixing that becomes a priority.
Fat Soluble Vitamins & CoQ10
All of these are needed for healthy metabolism, immune system function, and general function. They are need to restore healthy oxidative phosphorylation. CoQ10 is an essential part of the ETC and is needed for healthy metabolism. It is also especially important for heart health.
Vitamin A: Carrots, sweet potatoes, tomatoes, squash (all kinds), watermelon, asparagus, apples, apricots, prunes, papaya, kale, spinach, and broccoli. Carotene, or Provitamin A, is a major antioxidant, and is found in all warm-colored vegetables (red, orange, and yellow).
Vitamin D: Sunlight is the best source (it’s not even close). Food sources include sprouted seeds, alfalfa, mushrooms, sunflower seeds, and whole grains.
Vitamin E: Nuts, seeds, legumes, seaweed, and green leafy vegetables, brown rice, wheat germ, peas, lettuce, spinach, broccoli, asparagus, and avocados.
Vitamin K: Spinach, asparagus, tomatoes, carrots, kelp, alfalfa, green leafy vegetables, cabbage, and other vegetables in the cabbage family.
Coenzyme Q10: Broccoli, cauliflower, lentils, peanuts, most nuts and seeds, and spinach.
Breathwork
We previously talked about the importance of getting optimal amounts of CO2. Well, nasal breathing is what is going to help you get there. Filtration and humidifying effects of the nose on inhaled air and increased NO levels in the airways.
Your nose produces 10 parts per million (ppm) in the sinuses. During inspiration, NO will follow the airstream into the lower airways & lungs and diffuse throughout the tissues. This induces vasodilatory and bronchodilation effects.
Compared with oral breathing, inhalation of NO causes an overall significant blood flow shift from the base of the lung toward the apex. This results in more homogenous blood flow distribution along the height of the lung NO is scavenged by hemoglobin, so it is rapidly inactivated Once it reaches the blood. This simply means the effects of nasal NO are largely limited to the lungs.
In humans, higher basal levels of exhaled NO are associated with fewer symptoms of the common cold. Conditions associated with reduced nasal NO production are associated with recurrent respiratory infections and inflammation.
As I mentioned, my Breathe Easy course gives you the actionable steps!
Black Seed Oil
Not all seed oils are harmful!
Black seed (Nigella sativa) oil has a storied history (literally mentioned in the Torah, Bible, and Quran) in traditional medicine for a variety of uses, with virtually no side-effects.
It has several bioactive compounds that are thought to contribute to some of its many benefits. The first is thymoquinone, which is known for its antioxidant, anti-cancer, and anti-inflammatory properties. Thymoquinone has been shown to help manage blood sugar, asthma, and inhibit the development of cancer. Then we have thymol (which yes, is also found in thyme), which is a well-known antimicrobial and antiviral compound.
As it pertains to metabolism, black seed oil can help with the recycling of NAD+ to NADH, which is needed for healthy mitochondria function in the pancreas and elsewhere.
When you’re shopping for black seed oil, you want to make sure you’re getting a high quality one. Make sure it doesn’t include additives such as canola, sunflower, soybean and in general inferior fats. Ideally, there shouldn’t be any other ingredients.
I personally like Black Cumin Seed Forte by Mediherb (these are tablets) Organic Black Seed Oil by Heritage, or Black Seed Oil Gel Caps by Gaia Herbs. All of which you can purchase on my online dispensary here.
Wrapping Up
Creating a healthy environment that promotes optimal cellular function is incredibly important. Unfortunately, in the world we live in today, there are some factors we do not have control over. So we need to control the controllables to the best of our ability.
The water we drink, the air we take in, the foods we eat, the chemicals we encounter, and the electronic devices we use (cell phones, tablets, microwaves, X-rays) can all harm or heal to varying degrees, depending on our choices.
Conventional medicine and physiology frequently overlook the biophysical aspect of organic existence. This oversight persists despite the understanding that biochemical reactions, lacking regulatory and controlling information, would lead to metabolic chaos. We discussed how the current conventional model is insufficient in this blog.
Technology is now the driving of the American economy. For the economy to thrive, the health of the American people will suffer. This is our inconvenient reality.
This becomes clear when you grasp the functioning of mitochondria and the true findings of Dr. Otto Warburg. The implications for humanity are profound. Seeking solutions for a mitochondrial issue within the nuclear genome is a fundamental flaw. This is why the healthcare paradigm struggles to address the chronic disease challenges we face today.
It takes a perspective shift, and it starts on the individual level.
See you next week!
Dr. Vincent Esposito
Want More?
Whenever you’re ready, there are two ways I can help you:
- I’m excited to announce the launch of my new book: How to Get World Class Sleep! If you’ve struggled with insomnia, have trouble falling asleep, or wake up feeling sluggish, then this is for you! Fall Asleep Faster. Recover More Quickly. Wake Up Refreshed! Find it here!
- Start 2024 off right! Start Transforming Your Health 90 Days and apply for private one-on-one support here!